What Hygiene Standards Should Be Followed in Food Packaging?
What Hygiene Standards Should Be Followed in Food Packaging?
In the food industry, packaging plays a critical role not only in protecting products but also in ensuring their safety and hygiene. Adhering to strict hygiene standards during the packaging process is essential to prevent contamination and maintain consumer trust. So, what hygiene standards should be followed in food packaging? Let’s explore the key considerations.

1. Use of Food-Grade Materials
Packaging materials must comply with national and international food safety regulations, such as FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) or EU food contact material standards. These materials should be non-toxic, odorless, and chemically stable to avoid reactions with the food. Common choices include food-grade plastics, paper, and aluminum foil, which ensure freshness and protect the product from external influences.
2. Hygienic Design of Packaging Equipment
Packaging equipment must be designed to meet sanitary standards, ensuring easy cleaning and maintenance. Components that come into direct contact with food are typically made of 304 or 316 stainless steel, known for their rust-resistant and food-safe properties. Equipment should have no dead angles or hard-to-clean areas, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth.
3. Sterile Production Environment
Food packaging lines should operate in a controlled and sterile environment, especially for perishable items like dairy products or juices. Cleanrooms equipped with air filtration systems help maintain proper humidity and temperature levels. Regular cleaning and sanitization of the production area are critical, and personnel must wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves, masks, and hair nets to reduce contamination risks.
4. Stringent Quality Control
Thorough quality checks should be performed during the packaging process. This includes inspecting for issues like leaks, tears, or improper sealing. Metal detectors can identify foreign objects, and the accuracy of printed information, such as production dates and batch numbers, must be verified.
5. Anti-Contamination Packaging Design
Food packaging must protect products from external contamination, such as moisture, oxygen, insects, and UV light. For instance, vacuum-sealed or modified atmosphere packaging extends shelf life, while antimicrobial materials further reduce bacterial risks.
6. Compliance Certifications and Labels
All food packaging must meet relevant hygiene certifications, such as ISO 22000 Food Safety Management or HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points). These certifications not only guarantee hygiene but also build consumer confidence. Labels should clearly state product details, including ingredients, production date, expiry date, and storage instructions, ensuring transparency for customers.
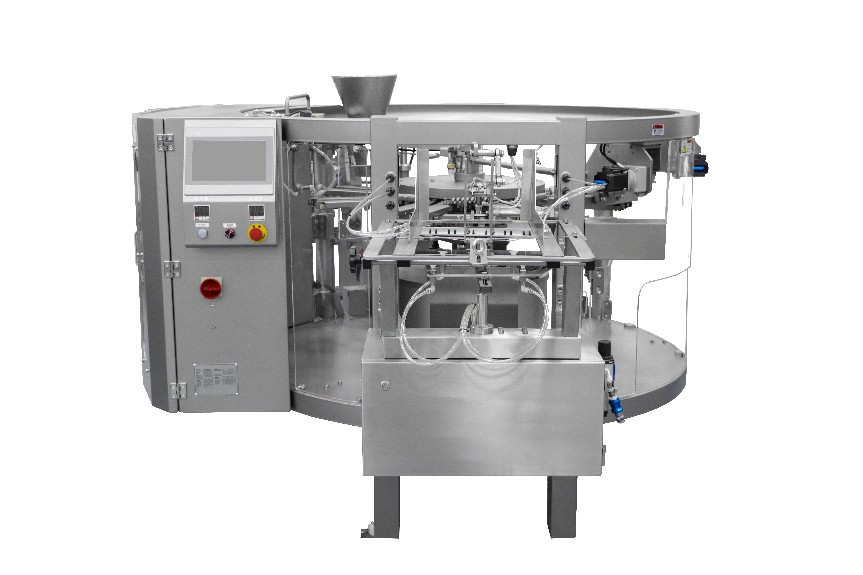
7.Role of Advanced Packaging Machines in Hygiene
Modern packaging machines play a vital role in ensuring hygienic food packaging. Automatic filling, sealing, and labeling processes minimize human contact with the product, significantly reducing contamination risks. Machines equipped with CIP (Clean-In-Place) systems ensure thorough cleaning of internal components, while features like UV sterilization or HEPA filters maintain hygiene during operation. Additionally, advanced machines allow manufacturers to handle sensitive products like liquids or powders with precision, maintaining hygiene standards across diverse packaging formats. By integrating smart sensors and automated monitoring, these machines detect and resolve potential hygiene issues in real time, ensuring safety and efficiency.

1. Use of Food-Grade Materials
Packaging materials must comply with national and international food safety regulations, such as FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) or EU food contact material standards. These materials should be non-toxic, odorless, and chemically stable to avoid reactions with the food. Common choices include food-grade plastics, paper, and aluminum foil, which ensure freshness and protect the product from external influences.
2. Hygienic Design of Packaging Equipment
Packaging equipment must be designed to meet sanitary standards, ensuring easy cleaning and maintenance. Components that come into direct contact with food are typically made of 304 or 316 stainless steel, known for their rust-resistant and food-safe properties. Equipment should have no dead angles or hard-to-clean areas, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth.
3. Sterile Production Environment
Food packaging lines should operate in a controlled and sterile environment, especially for perishable items like dairy products or juices. Cleanrooms equipped with air filtration systems help maintain proper humidity and temperature levels. Regular cleaning and sanitization of the production area are critical, and personnel must wear appropriate protective gear such as gloves, masks, and hair nets to reduce contamination risks.
4. Stringent Quality Control
Thorough quality checks should be performed during the packaging process. This includes inspecting for issues like leaks, tears, or improper sealing. Metal detectors can identify foreign objects, and the accuracy of printed information, such as production dates and batch numbers, must be verified.
5. Anti-Contamination Packaging Design
Food packaging must protect products from external contamination, such as moisture, oxygen, insects, and UV light. For instance, vacuum-sealed or modified atmosphere packaging extends shelf life, while antimicrobial materials further reduce bacterial risks.
6. Compliance Certifications and Labels
All food packaging must meet relevant hygiene certifications, such as ISO 22000 Food Safety Management or HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points). These certifications not only guarantee hygiene but also build consumer confidence. Labels should clearly state product details, including ingredients, production date, expiry date, and storage instructions, ensuring transparency for customers.
7.Role of Advanced Packaging Machines in Hygiene
Modern packaging machines play a vital role in ensuring hygienic food packaging. Automatic filling, sealing, and labeling processes minimize human contact with the product, significantly reducing contamination risks. Machines equipped with CIP (Clean-In-Place) systems ensure thorough cleaning of internal components, while features like UV sterilization or HEPA filters maintain hygiene during operation. Additionally, advanced machines allow manufacturers to handle sensitive products like liquids or powders with precision, maintaining hygiene standards across diverse packaging formats. By integrating smart sensors and automated monitoring, these machines detect and resolve potential hygiene issues in real time, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)